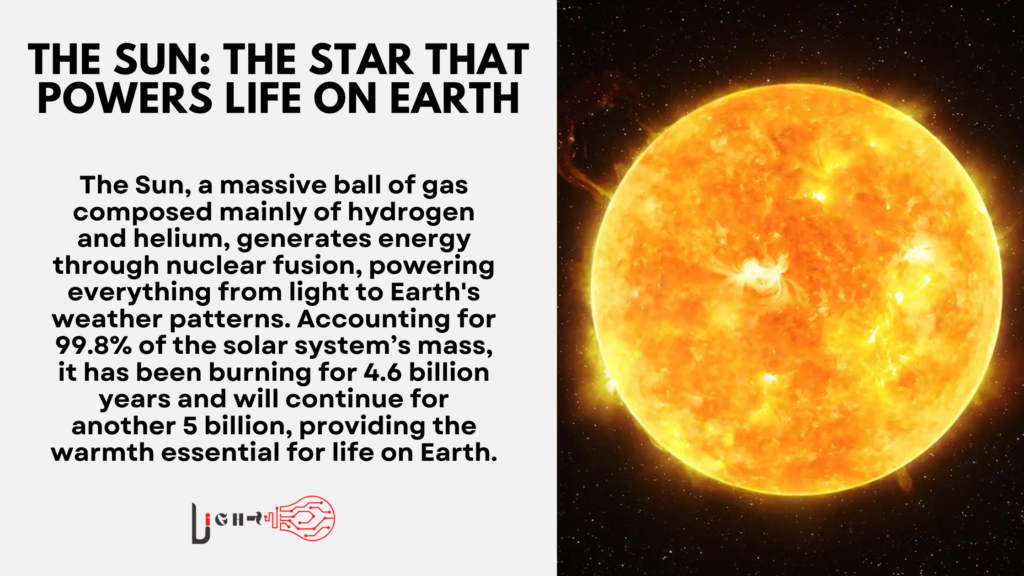
The Sun is the centerpiece of our solar system. It is a massive, glowing ball of gas, primarily composed of hydrogen and helium. Its core generates energy through nuclear fusion, a process where hydrogen atoms fuse to create helium, releasing an immense amount of energy in the form of light and heat. This energy radiates outward, fueling everything from the light we see to the weather patterns that shape our planet.
As a star, the Sun is relatively average in size, but it accounts for 99.8% of the total mass of our solar system. It’s approximately 4.6 billion years old and is expected to continue burning for another 5 billion years. The light from the Sun takes about eight minutes to reach Earth, providing the warmth necessary for life. Without the Sun, Earth would be a cold, lifeless rock floating in space.
The Sun’s Role in the Solar System
The Sun doesn’t just provide light and warmth. Its gravitational pull keeps all the planets, moons, and other celestial objects in their respective orbits. Without the Sun’s gravity, the planets would drift off into space. It serves as the anchor of our solar system, maintaining balance and order.
Beyond that, the Sun also influences space weather. Solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs) are bursts of solar energy and particles that can disrupt satellites, power grids, and communication systems on Earth. While these events are rare, they remind us of the Sun’s tremendous power, both in its ability to sustain life and to potentially cause disruptions.
Aravalli Mountains: Exploring India’s Ancient Range
To know more click here:https://light.vintbit.com/inter-national-gk/aravalli-mountains-oldest/
How the Sun Affects Earth’s Climate and Weather
The Sun is the primary driver of Earth’s climate and weather. Solar radiation heats the Earth’s surface, causing air and water to move, creating the wind and ocean currents that we experience as weather. Over long periods, changes in the Sun’s energy output can lead to natural climate variations, such as ice ages or periods of warming.
The Earth’s tilt on its axis means that different parts of the planet receive varying amounts of sunlight throughout the year. This is what creates the seasons. The Sun’s energy is also responsible for generating storms, as warm air rises, cools, and condenses to form clouds and precipitation.
Influence on Seasons and Weather Patterns
Seasons change due to the Earth’s tilt and orbit around the Sun. When a hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun, it experiences summer, with longer days and more direct sunlight. Conversely, when tilted away, winter sets in. The Sun’s angle and intensity determine weather patterns, influencing temperature variations, storm formations, and overall climate conditions across the globe.
Solar Energy: Harnessing the Power of the Sun
One of the greatest ways humanity benefits from the Sun is through solar energy. By converting sunlight into electricity using solar panels, we harness a clean and renewable energy source. This process involves photovoltaic (PV) cells, which absorb sunlight and convert it into electrical power, reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and cutting greenhouse gas emissions.
Solar power has become increasingly efficient and affordable over time, making it an attractive option for homes and businesses. Many countries are now investing heavily in solar farms, which can power entire communities and reduce the carbon footprint associated with energy production.
Benefits of Solar Power for Homes and Businesses
Solar power offers numerous advantages. For homes, it can significantly lower electricity bills, especially in sunny regions. Installing solar panels allows homeowners to generate their own electricity, reducing dependence on the grid. For businesses, solar power can cut operational costs and boost sustainability credentials, attracting eco-conscious consumers. Furthermore, governments often provide incentives and tax breaks for those who invest in solar technology, making it a financially viable option for many.
The Sun’s Role in Supporting Life on Earth
The Sun is essential to life on Earth. Its light and warmth create the conditions necessary for life to exist, from tiny microorganisms to large mammals. Plants rely on sunlight for photosynthesis, the process by which they convert light into chemical energy. This energy, in turn, supports the entire food chain, making the Sun the ultimate source of all life on our planet.
Humans also depend on the Sun for vitamin D synthesis, which is vital for bone health and overall well-being. The Sun’s influence on circadian rhythms also regulates our sleep patterns and mood.
How Photosynthesis Relies on the Sun
Photosynthesis is the process where plants absorb sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce oxygen and glucose. This process is the foundation of most ecosystems, as it provides the energy needed for plants to grow, which herbivores eat, and which in turn are consumed by carnivores. Without the Sun, photosynthesis would cease, and the food chain would collapse, leading to the extinction of most life forms.1
Facts about Sun
The Sun, with a surface temperature of around 5,500 degrees Celsius (9,932 degrees Fahrenheit), is much more than just a bright light in the sky. It fuels life on Earth, drives our weather systems, and offers a sustainable energy source for the future. Remarkably, every second the Sun generates enough energy to power our planet for 500,000 years. In the distant future, it will expand into a red giant, engulfing Mercury and Venus, before eventually shrinking into a white dwarf. Understanding the Sun’s immense power and role helps us appreciate the delicate balance that sustains life on Earth.