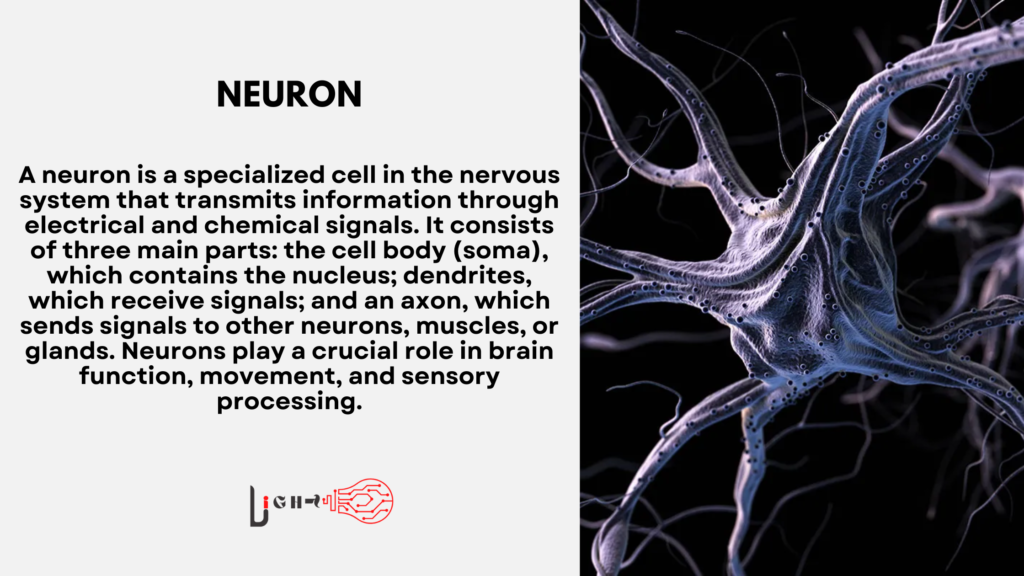
A neuron is a specialized cell that forms the foundation of the nervous system. These cells are responsible for transmitting electrical and chemical signals, enabling communication between the brain, spinal cord, and the rest of the body.
Neurons play a crucial role in everything from reflex actions to complex cognitive functions. Unlike other cells, neurons do not regenerate easily, making their function and health vital to overall well-being.
Structure of a Neuron
Neurons have a unique structure that allows them to send and receive signals efficiently. Each neuron consists of several key components that contribute to its function.
Cell Body (Soma)
The cell body, or soma, houses the nucleus and is responsible for maintaining the neuron’s overall function. It produces proteins and energy required for signal transmission.
Dendrites
Dendrites are tree-like extensions from the cell body that receive signals from other neurons. These structures increase the surface area of the neuron, allowing it to form multiple connections.
Rachel Carson: The Scientist Who Changed Environmental Awareness
To know more click here:https://light.vintbit.com/general-knowledge/rachel-carson-biologist/
Axon
The axon is a long, slender projection that carries signals away from the cell body. It can vary in length, with some axons extending several feet, such as those connecting the spinal cord to the toes.
Myelin Sheath
The myelin sheath is a protective covering around the axon that speeds up signal transmission. This fatty layer ensures that electrical impulses travel quickly and efficiently along the neuron.
Types of Neurons
Neurons are classified into different types based on their function in the nervous system.
Sensory Neurons
Sensory neurons carry information from sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord. They help process stimuli such as touch, temperature, and pain, allowing the body to respond appropriately.
Motor Neurons
Motor neurons transmit signals from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands. These neurons are responsible for voluntary and involuntary movements, including reflex actions.
Interneurons
Interneurons connect sensory and motor neurons within the central nervous system. They play a key role in processing information and enabling coordinated responses.
How Neurons Communicate
Neurons communicate through a combination of electrical and chemical signals. This process, known as synaptic transmission, involves several steps:
- Electrical Impulse Generation – A neuron generates an electrical signal called an action potential.
- Signal Transmission – The action potential travels down the axon to the synapse.
- Neurotransmitter Release – At the synapse, neurotransmitters are released into the gap between neurons.
- Signal Reception – The next neuron receives the neurotransmitters, triggering a new electrical signal.
This rapid communication allows the brain to process information and send instructions to the body in milliseconds.
Importance of Neurons in Brain Function
Neurons are fundamental to all brain activities, including memory, learning, and decision-making. They form complex networks that store and retrieve information, enabling cognitive processes.
Damage to neurons can lead to neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis. Maintaining neural health through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and mental stimulation is essential for brain function.
Conclusion
Neurons are the essential components of the nervous system, enabling communication between the brain and body. Their structure and function allow for complex processes like movement, sensation, and thought. Understanding neurons helps us appreciate their role in maintaining overall health and well-being.