Earth’s constant movement in space plays a crucial role in shaping life as we know it. Two primary motions define this movement: rotation and revolution. Rotation is the spinning of Earth on its axis, which causes day and night. Revolution, on the other hand, refers to Earth’s journey around the Sun, responsible for the changing seasons. Both of these motions are integral to the planet’s environmental and climatic patterns. In this blog, we will explore the differences between these two movements and their impact on life on Earth.
What is Earth’s Rotation?
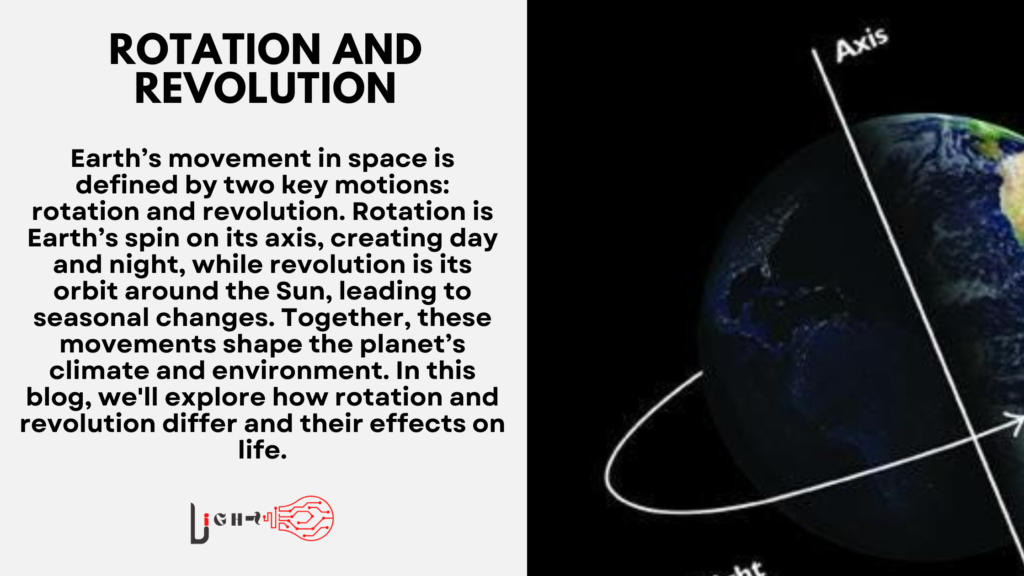
Earth’s rotation refers to the spinning of the planet around its own axis. This axis is an imaginary line that runs from the North Pole to the South Pole, tilted at approximately 23.5 degrees. It takes Earth about 24 hours to complete one full rotation, which is why we experience day and night.
As Earth rotates, different parts of the planet are exposed to sunlight, resulting in daytime for one hemisphere while the other is in darkness, experiencing night. This consistent rotation creates a regular pattern of day and night that has shaped biological rhythms and timekeeping systems across human history. Without Earth’s rotation, one side of the planet would be in permanent daylight, while the other side would remain in perpetual darkness, drastically affecting life as we know it.
Earth’s Axis of Rotation
The tilt of Earth’s axis is responsible for various seasonal effects. Although rotation itself doesn’t cause the seasons, it does play a role in how sunlight is distributed across the globe. The tilt allows for different angles of sunlight during Earth’s revolution around the Sun, which we will explore in more detail below.
What is the Earth’s Revolution?
Earth’s revolution is the elliptical orbit that it takes around the Sun. It takes approximately 365.25 days to complete one full revolution, which is why we have leap years to account for the extra quarter-day. This motion is responsible for the changing seasons throughout the year.
As Earth revolves around the Sun, its axial tilt causes different hemispheres to receive varying amounts of sunlight. When the Northern Hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun, it experiences summer, while the Southern Hemisphere experiences winter, and vice versa. This cycle of revolution has a profound effect on the climate, agriculture, and overall environmental patterns that sustain life on Earth.
Earth’s Orbit Around the Sun
The path Earth follows around the Sun is not a perfect circle but an ellipse, meaning that the distance between Earth and the Sun varies throughout the year. However, this variation in distance does not significantly affect the temperature. Instead, it’s the tilt of Earth’s axis and the angle of sunlight that drive seasonal changes.
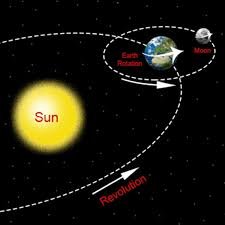
Differences Between Rotation and Revolution
While both rotation and revolution are critical to Earth’s functioning, they differ in several key ways. Rotation occurs on an axis, while revolution involves an orbit around the Sun. Rotation takes just 24 hours, while revolution takes a full year.
In terms of impact, rotation governs the day-night cycle, while revolution causes the seasons. The speed at which these movements occur also varies, with rotation happening much faster than revolution. These differences, though subtle, have a massive influence on how life is structured on Earth.1
Impact of Earth’s Rotation on Life
Earth’s rotation affects not just the cycle of day and night but also weather patterns, ocean tides, and even the Coriolis effect, which influences wind direction. Without this rotation, life on Earth would be drastically different. The natural cycle of light and dark regulates everything from sleep patterns in animals to the growth of plants. Ocean currents and wind systems are also tied to the rotation of Earth, helping distribute heat and moisture around the globe, which is essential for maintaining climates that support biodiversity.
E. K. Nayanar: The People’s Chief Minister of Kerala
To know more click here:https://light.vintbit.com/general-knowledge/e-k-nayanar-political-leader/
Impact of Earth’s Revolution on Seasons
Earth’s revolution plays a central role in creating the seasons. As the planet moves around the Sun, the tilt of its axis causes different parts of the world to receive more or less sunlight. This results in the temperature changes we associate with summer, autumn, winter, and spring.
For example, during the summer solstice, the Northern Hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun, receiving more direct sunlight and longer days, leading to warmer temperatures. Conversely, during the winter solstice, the same hemisphere is tilted away from the Sun, resulting in shorter days and cooler temperatures. These seasonal shifts have a significant impact on agriculture, ecosystems, and human activity.
Conclusion: The Role of Rotation and Revolution in Planetary Motion
Understanding Earth’s rotation and revolution helps us appreciate how these fundamental motions affect life on our planet. The day-night cycle and the seasons are just two of the most visible consequences of these movements. Together, they regulate not only the environment but also the rhythms of life, allowing Earth to sustain a rich and diverse ecosystem.